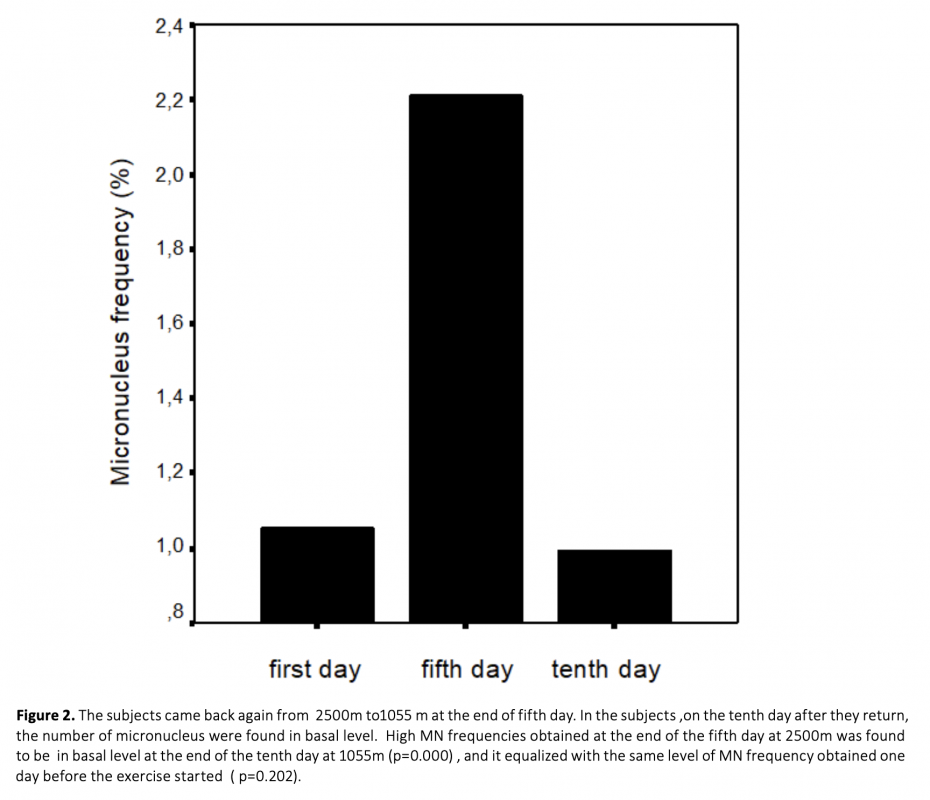
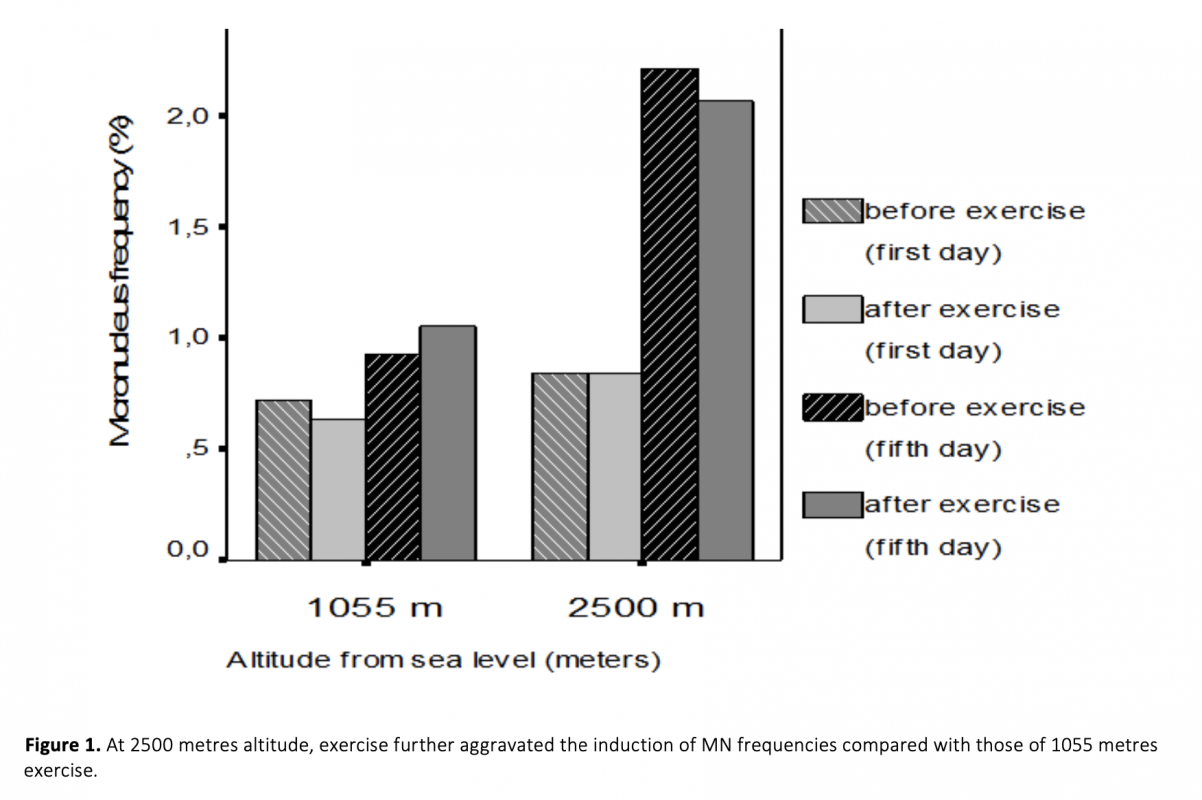
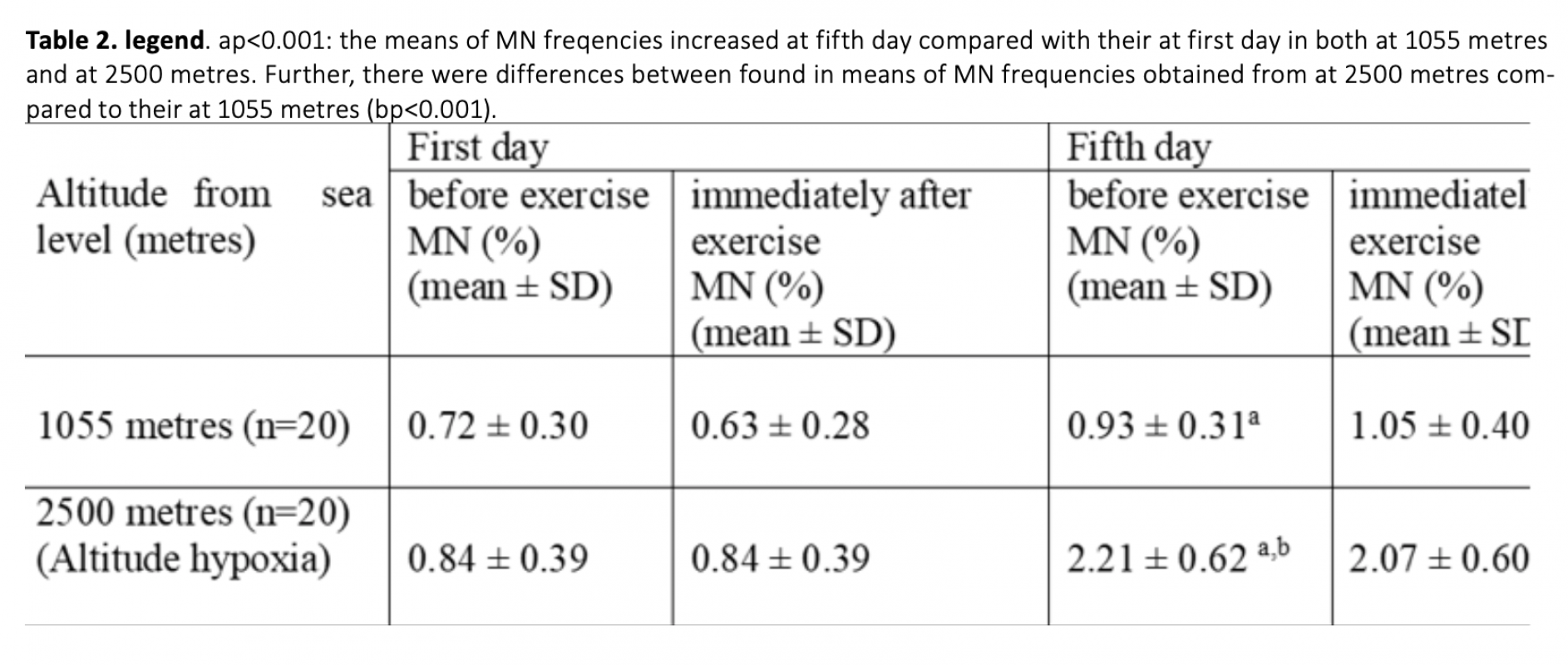
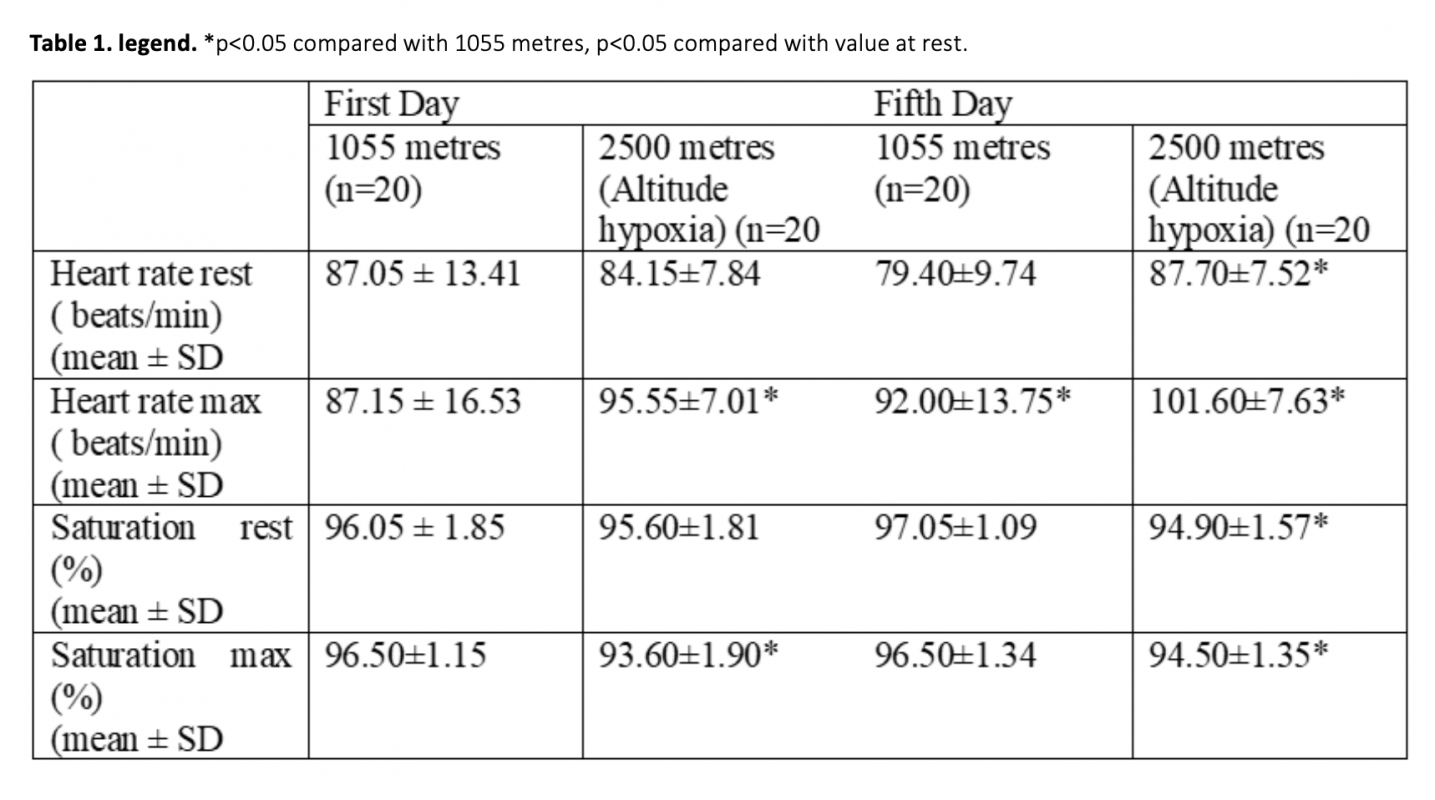
High altitude hypoxia and hypoxic exercise may induce oxidative DNA damage.Our study was investigated the effect on the micronucleus (MN) frequency of performed exercise at 1055m and at 2500m. MN frequency is a biomarker of chromosomal damage, genome instability. 10 female and 10 male totally 20 subject were included in the study. They performed exercise 3 hours per day during 5 days at each two location. The peripheral blood samples obtained before exercise and immediately after the exercise at 1055 m and 2500 m altitude both first day and fifth day were cultured. The number of MN values was scored in binucleated cells obtained from mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes of subjects. We found that exercise performed at 1055m conditions induced MN formation (p<0.001); whereas exercise performed at 2500m induced more MN formation in human lymphocytes (p<0.001). In addition , in the subjects after ten days came back down to 1055 m from the mountain MN frequencies was decreased that those of at the end of the five day at 2500 m altitude (p<0.001). Also, this MN frequency was similar to with basal MN frequency at 1055 m (p>0.05).Our results indicated that exercise and altitude may cause chromosomal DNA damage and may be closely relative to mutagenic effects.
Yüksek irtifa hipoksi ve hipoksik egzersiz oksidatif DNA hasarına neden olabilir. Çalışmamız 1055m ve 2500m’de yapılan egzersizin mikronükleus (MN) sıklığı üzerindeki etkisi araştırıldı. MN frekansı, kromozomal hasarın, genom kararsızlığının bir biyolojik işaretidir. 10 erkek, 10 kadın toplam 20 sağlıklı denek çalışmaya dahil edildi. Her iki yerde 5 gün boyunca günde 3 saat egzersiz yaptılar. Egzersizden önce ve egzersizden hemen sonra 1055 m ve 2500 m yükseklikte periferik kan örnekleri hem birinci hem de beşinci günde kültürlendi. Hastaların mitojenle uyarılmış lenfositlerinden elde edilen çift çekirdekli hücrelerde MN değerlerinin sayısı kaydedildi. 1055m koşullarında yapılan egzersizin MN oluşumunu indüklediğini bulduk (p <0.001); 2500 m’de yapılan egzersiz, insan lenfositlerinde daha fazla MN oluşumuna neden olmuştur (p<0.001). Ayrıca, on gün sonra dağdan 1055m’ye geri inen deneklerin MN frekansları, beş günün sonunda 2500 m rakımdakinden daha düşüktü (p <0.001). Ayrıca, bu MN frekansı, 1055 m’deki bazal MN frekansına benzerdi (p> 0.05). Sonuçlarımız egzersiz ve rakımın kromozomal DNA hasarına neden olabileceğini ve mutajenik etkilere yakından görülebileceğini göstermiştir.
Download Article in PDF (430.9 kB)